
Back in December 2015 I spent a couple of weeks in the Wakatobi, Indonesia, initiating phase II of the Wakatobi Seagrass Program. This seeks to build on work carried out though a previous project “Recognising the role of seagrass meadows in food security: re-prioritising the marine conservation agenda” (2011-2014), which was conducted in the same location.
That project evidenced the direct economic value and food security potential of seagrass meadows and prompted local government and community stakeholders to place seagrass on their conservation agendas for the first time. The Wakatobi project demonstrated how seagrass associated species provide an essential source of protein and income to the vast majority of people in the region. We provided evidence of the links between seagrass and food security and highlighted that these currently expansive ecosystems remain largely ignored within formal legal or environmental management frameworks, even within an MPA at the heart of the Coral Triangle.

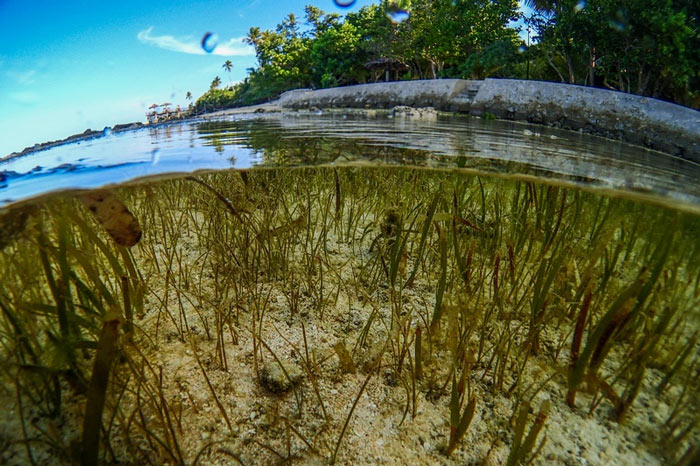
Seagrass meadows provide an essential source of protein and income to the vast majority of people in the region.
The outputs from the first project are being used to drive forward discussions between local stakeholders to bring about change. And although their value is somewhat recognised in the Wakatobi, these expansive ecosystems are threatened by a myriad of anthropogenic activities. The host of threats at play within the Wakatobi range from mangrove destruction to overfishing and aren’t going to disappear overnight. Phase II of the Wakatobi Seagrass Program seeks to work on these threats through local, community level action, and devising strategies to work with formed the basis of my trip.

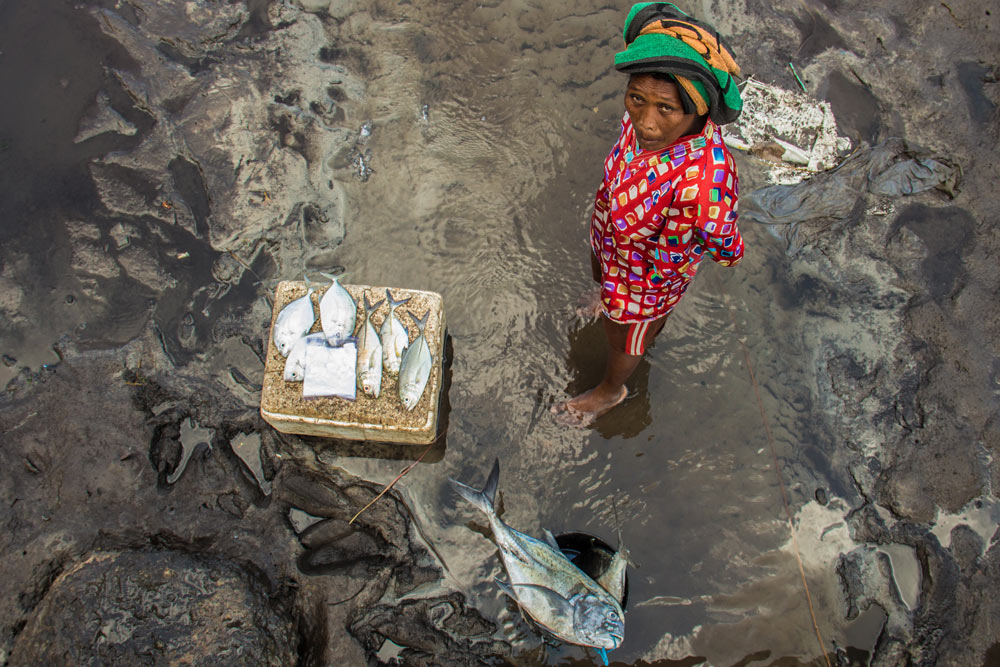
Seagrass meadows across the Wakatobi are threatened by a host of factors. Overfishing has left many meadows lifeless.
As communications developed with our local partner, FORKANI, it seemed clear that one of the issues they felt was dominant, was the issue of run-off. Terrestrial run-off causes huge problems for seagrass through both sedimentation and eutrophication, and as the destruction of mangroves (15% of mangrove forest has been destroyed by local community members seeking firewood and construction materials) and forest areas continues, the ability for land to absorb and store water lessens. Given this, FORKANI proposed an exciting idea to rehabilitate both mangrove and forest areas around rivers in 3 key villages, not only to reduce impact on seagrass but to improve the continually worsening problem of water storage on the island of Kaledupa.
However, with so much forest now converted to palm plantations, choosing areas to rehabilitate wasn’t going to be an easy task, and choosing areas that were key was even harder. FORKANI were amazingly resourceful when it came to the practicalities of choosing locations, mapping each river in a way that made it easy to pin point areas that needed the most work. Sometimes working the old fashioned was has its perks, and the relative ease in which they categorised each river was efficient and effective. FORKANI have now chosen areas to rehabilitate and are currently working on preparing the areas and seedlings, while also beginning to monitor seagrass in front of each village to track their own progress.
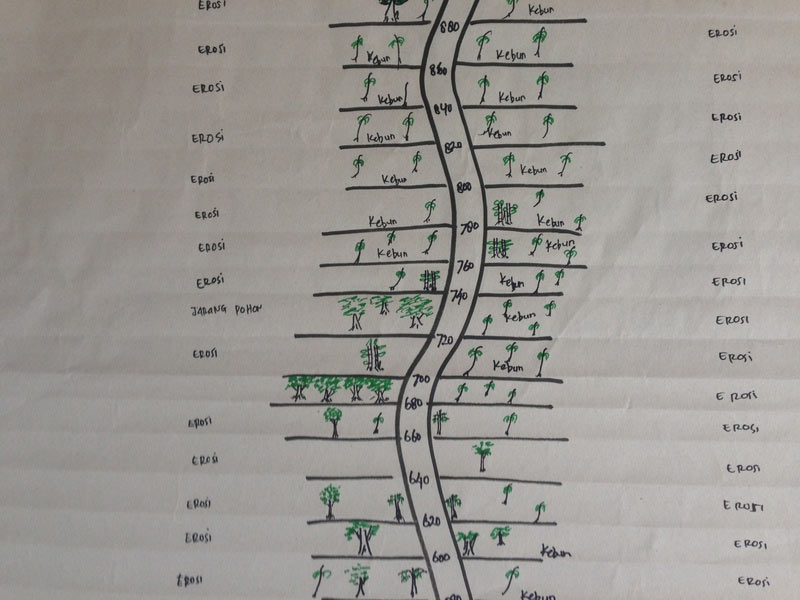
Conducting river mapping was efficient and effective and allowed FORKANI to choose key areas for rehabilitation
Even though discussions were productive, overfishing is still the “elephant in the room” that nobody wants to talk about. Although dynamite and cyanide fishing are now almost absent across the national park, at least that’s what we’re told, the unsustainable removal of juvenile fish is still a widespread issue. Fish fences, or “sero” as they are locally called, are one of the biggest issues facing the Wakatobi National Park and tentative UNESCO World Heritage Site. These fish fences, scar’s upon the face of the park’s beauty, fish 24/7 and, as we’ve discovered, are not only restricted to seagrass meadows.
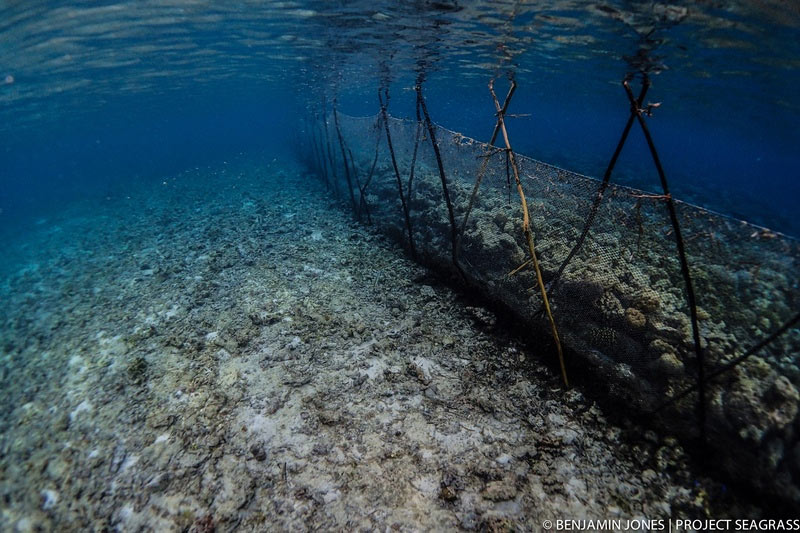

Fish fences have left both reefs and seagrasses looking like barren wastelands.
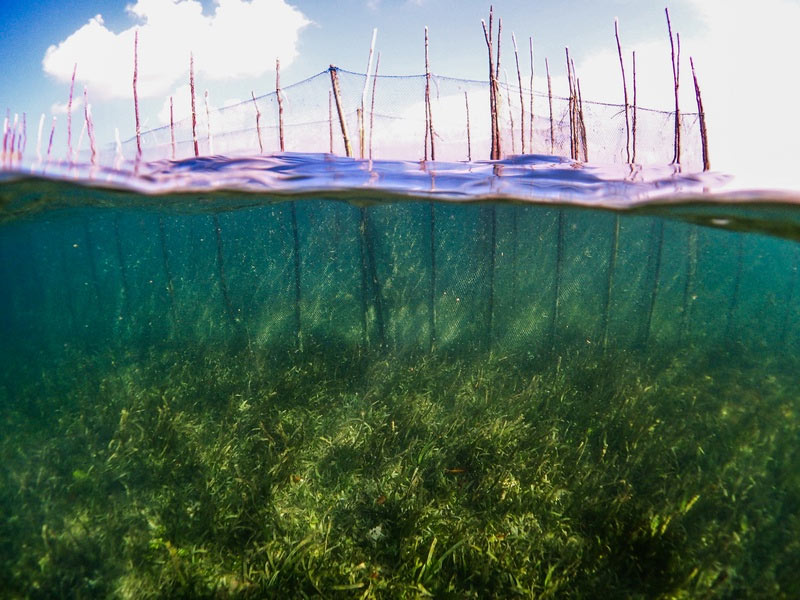

Fishing 24/7. The Sero are non selective and never stop fishing
Tackling the overfishing problem will take time, but by tapping into the past, we can begin to improve the future of the Wakatobi’s coastal fisheries. For centuries, isolated communities across the globe have respected a delicate balance with the ocean — taking fish only from certain areas, of certain sizes and with specific methods to maintain a healthy ecosystem and supply of fish for present and future. Now, with two key fishing villages keen to work on adopting community managed no-take areas there is some serious hope for the future. This solution, which builds on and adapts successful fisheries management techniques, provides a win-win for coupled socio-ecological systems, protecting fishers wellbeing as well as the health of marine ecosystems. Systems like this, that are well-managed, result in more fish — and not just by a few. By adopting this formula, and continually managing their fishery, communities can expect to see a potential increase of up to 56 percent in fish abundance and a potential increase in yield of up to 40%.
In 2006, then Indonesian President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono made a hugely ambitious promise to conserve a “global epicentre of marine life abundance and diversity”, stating that Indonesia would preserve 10 million hectares of ocean lying in the Coral Triangle. In 2009, he doubled this commitment to 20 million hectares by 2020. The the 1.39 million hectare Wakatobi National Park contributes to the 16.6 million hectares already protected – but given the status of seagrasses and the vast overfishing problem, serious questions about the meaning ‘protected’ arise. Is the Wakatobi destined to become a site of World Heritage value or just a wasteland?
The Wakatobi’s communities are centre to answering this question. Although their sense of ownership always has been present, with these proposed mitigation measures being taken a little more seriously by communities, its clear that with a little motivation the people of Kaledupa can be tremendously proactive. This gives us a glimmer of hope for seagrass in this dynamic region of the world.
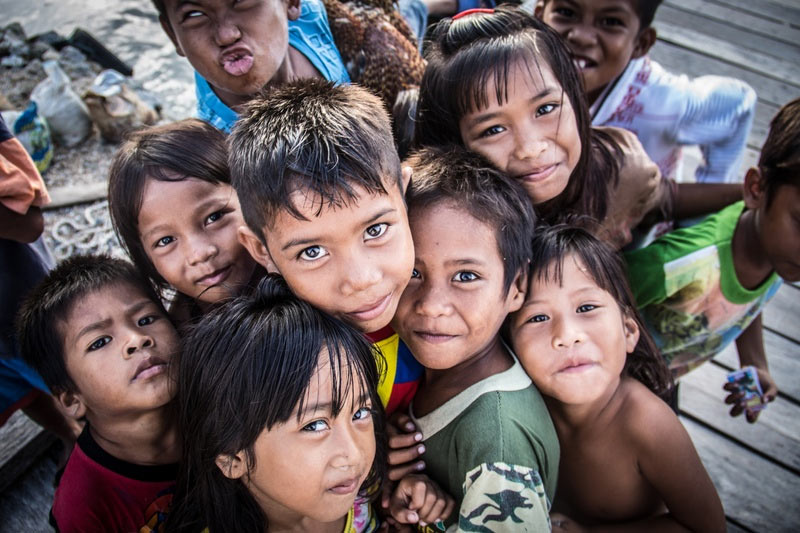

The future of the Wakatobi is dependent on its communities, yet the communities are dependent on the future of the Wakatobi itself.

