How eelgrass spread around the world
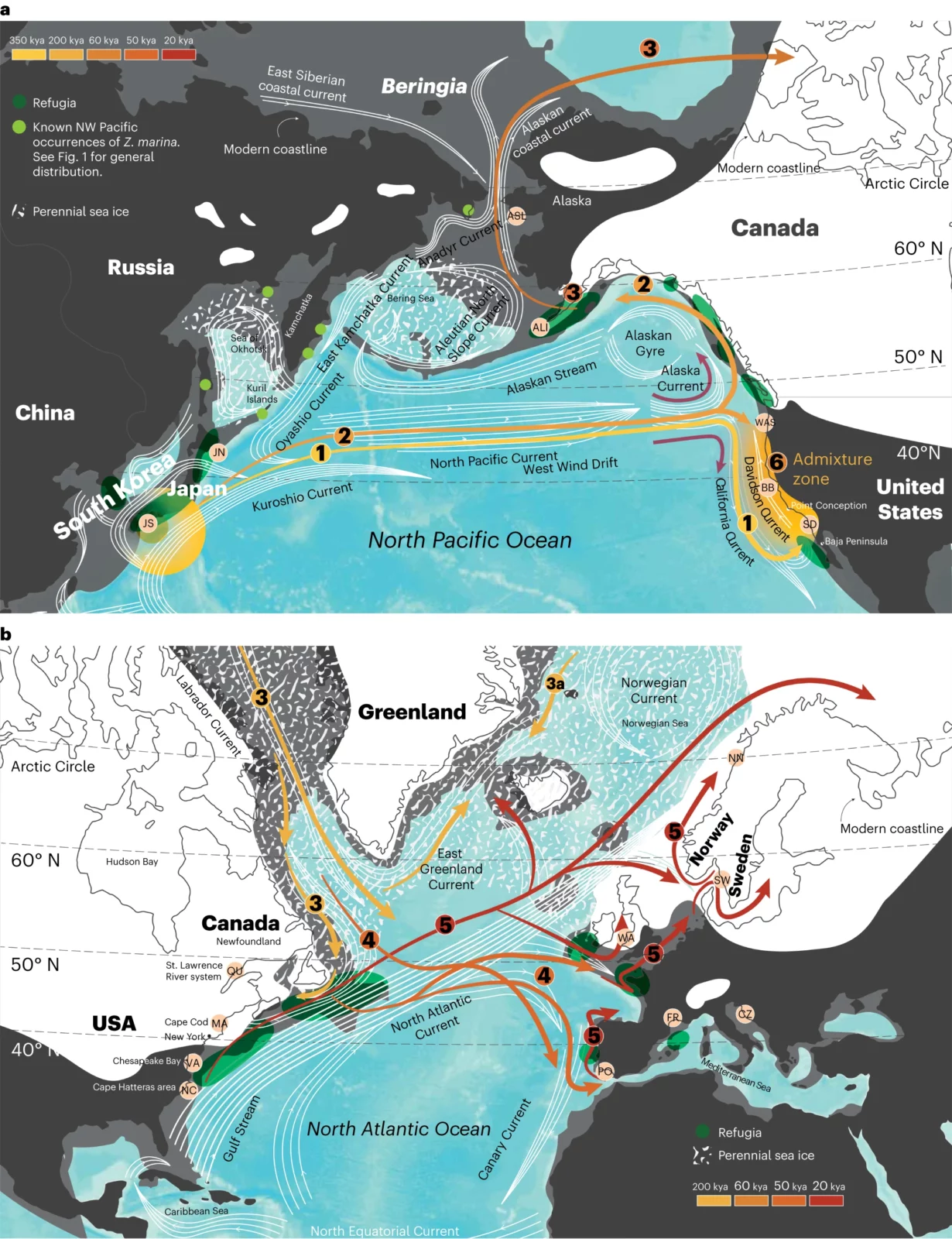
Seagrasses evolved from freshwater plants and use sunlight and carbon dioxide (CO2) for photosynthesis and are able to thrive in depths down to 50 meters. In contrast to algae, they possess roots and rhizomes that grow in sandy to muddy sediments. The grass-like, leaf-shoots produce flowers and complete their life cycle entirely underwater. Seeds are negatively buoyant but seed-bearing shoots can raft, thus greatly enhancing dispersal distances at oceanic scale. As a foundational species, eelgrass (Zostera marina) provides critical shallow-water habitats for diverse biotas and also provides numerous ecosystem services including carbon uptake. Seagrasses have recently been recognized as one of the important nature-based contributions to store carbon in the ocean. The sediment below seagrass meadows can sequester between 30 and 50 times more carbon annually that the roots of forests on land. Unfortunately, the continuing loss of seagrass beds worldwide—including eelgrass—is of acute concern. An international group of researchers, including Richard Unsworth and coordinated by Professor Thorsten Reusch, Head of the Research Division Marine Ecology at GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, used complete nuclear and chloroplast genomes from 200 individuals and 16 locations to reconstruct and date the colonisation history of the eelgrass Zostera marina from its origin in the Northwest Pacific Ocean to the Pacific, Atlantic and the Mediterranean. The findings described in an article and a Research Briefing published in Nature Plants beg the question, “How well will eelgrass adapt to our new, rapidly changing climate?” Using a phylogenomic approach the scientists were able to determine that Z. marina first arose in the Japanese Archipelago region and then crossed the Pacific from west to east in at least two colonisation events, probably supported by the North Pacific Current. The scientists then applied two DNA “molecular clocks”—one based on the nuclear genome and one based on the chloroplast genome—to deduce the time when eelgrass populations diverged into new ones. The DNA mutation rate was calculated and calibrated against an ancient, whole genome duplication that occurred in eelgrass. Both nuclear and chloroplast genomes revealed that eelgrass dispersed to the Atlantic through the Canadian Arctic about 243 thousand years ago. This arrival is far more recent than expected—thousands of years versus millions of years, as is the case with most Atlantic immigrant species during the Great Arctic Exchange some 3.5 million years ago. Reusch explains, “We thus have to assume that there were no eelgrass-based ecosystems—hotspots of biodiversity and carbon storage—in the Atlantic before that time. Recency was also mirrored in an analysis of the associated faunal community, which features many fewer specialized animals in the Atlantic as compared to the Pacific eelgrass meadows. This suggests that there was less time for animal-plant co-evolution to occur.” Mediterranean populations were founded from the Atlantic about 44 thousand years ago and survived the Last Glacial Maximum. By contrast, today’s populations found along the western and eastern Atlantic shores only (re)expanded from refugia after the Last Glacial Maximum, about 19 thousand years ago—and mainly from the American east coast with help from the Gulf Stream. In addition, the researchers further confirmed the huge difference in genomic diversity between the Pacific and Atlantic, including latitudinal gradients of reduced genetic diversity in northern populations. “Both Atlantic compared to Pacific populations, and northern versus southern ones are less diverse on a genetic level than their ancestors by a factor of 35 among the most and least diverse one,” said postdoctoral scientist Dr. Lei Yu, first author of the publication, which was a chapter in his doctoral thesis. “This is due to bottlenecks arising from past ice ages, which raises concerns as to how well Atlantic eelgrass, will be able to adapt to climate change and other environmental stressors based on its genetic capacity.” “Warming oceans have already caused losses of seagrass meadows at the southern range limits, in particular North Carolina and southern Portugal. In addition, heat waves have also caused losses in shallow waters in some the northern parts of the distribution,” noted Reusch. “This is not good news because seagrass meadows form diverse and productive ecosystems, and no other species is able to take on the role of eelgrass if meadows cannot persist under future conditions.” “One possibility for restoration might be to borrow some genetic diversity from Pacific eelgrass to fortify diversity in the Atlantic. Our next step is to interrogate the eelgrass pangenome. A new reference genome from Pacific eelgrass is currently under development and should tell us more about the adaptive ecotypic capacity across its global range of habitats,” said Prof. Jeanine Olsen, emeritus professor from the University of Groningen who initiated the study and coordinated the work between the Joint Genome Institute (JGI) and the research team. More information: Yu, L. etal, Ocean current patterns drive the worldwide colonization of eelgrass (Zostera marina), Nature Plants (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41477-023-01464-3 Story provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres
Legacy of ancient ice ages shapes how seagrasses respond to environmental threats today

Deep evolution casts a longer shadow than previously thought, scientists report in a new paper published the week of Aug. 1 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Smithsonian scientists and colleagues looked at eelgrass communities—the foundation of many coastal marine food webs along the north Atlantic and Pacific coasts—and discovered their ancient genetic history can play a stronger role than the present-day environment in determining their size, structure and who lives in them. And this could have implications for how well eelgrasses adapt to threats like climate change. About a half-million years ago, when the world was warmer, some eelgrass plants made the difficult journey from their homes in the Pacific to the Atlantic. Not all the plants were hardy enough to make the journey across the Arctic. For those that succeeded, a series of ice ages during the Pleistocene Epoch further affected how far they could spread. Those millennia-old struggles left lasting signatures in their DNA: Even today, eelgrass populations in the Atlantic are far less genetically diverse than those in the Pacific. Still, in the classic “nature versus nurture” debate, scientists were stunned to discover that genetic legacy sometimes does more to shape modern eelgrass communities than the current environment. “We already knew that there was big genetic separation between the oceans, but I don’t think any of us ever dreamed that that would be more important than environmental conditions,” said Emmett Duffy, marine biologist with the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center and lead author of the report. “That was a big surprise to everybody.” Eelgrasses in hot water Eelgrass is among the most widespread shallow-water plants in the world. Its range spans from semi-tropical regions like Baja California all the way to Alaska and the Arctic. Besides providing food and habitat for many undersea animals, eelgrass offers a plethora of services to humans. It protects coastlines from storms, soaks up carbon and can even reduce harmful bacteria in the water. But in most places where it grows, eelgrass is the dominant—or only—seagrass species present. That makes its survival critical to the people and animals that live there. And the lower genetic diversity in the Atlantic could make it hard for some populations to adapt to sudden changes. “Diversity is like having different tools in your tool belt,” said Jay Stachowicz, a co-author and ecologist with the University of California, Davis. “And if all you’ve got is a hammer, you can put in nails, but that’s about it. But if you have a full complement of tools, each tool can be used to do different jobs more efficiently.” Ecologists have already seen eelgrass disappearing from some regions as the waters heat up. In Portugal, its southernmost spot in Europe, eelgrass has begun pulling back and moving farther north, into cooler waters. “I don’t think that we’re going to lose [eelgrass] in the sense of an extinction,” said co-author Jeanine Olsen, an emeritus professor at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands. “It’s not going to be like that. It’s got lots of tricks up its sleeve.” But local extinctions, she pointed out, are going to occur in some places. That could leave regions that depend on their local eelgrass in trouble. Reaching a more ZEN worldview Realizing the urgent need to understand—and conserve—eelgrass worldwide, Duffy and his colleagues banded together to form a global network called ZEN, which Project Seagrass was a partner of. The name stands for Zostera Experimental Network, a nod to eelgrass’s scientific name, Zostera marina. The idea was to unite seagrass scientists all over the world, doing the same experiments and surveys, to get a coordinated global picture of seagrass health. For the new study, the team studied eelgrass communities at 50 sites in the Atlantic and Pacific. With 20 plots sampled per site, the team came away with data from 1,000 eelgrass plots. First they collected basic eelgrass data: size, shape, total biomass and the different animals and algae living on and around them. Then they collected genetic data on all the eelgrass populations. They also measured several environmental variables at each site: temperature, the water’s saltiness and nutrient availability, to name just a few. Ultimately, they hoped to discover what shaped eelgrass communities more: the environment or the genetics? After running a series of models, they discovered a host of differences between the Atlantic and Pacific eelgrass ecosystems—differences that closely aligned with the genetic divergence from the Pleistocene migration and subsequent ice ages. While Pacific eelgrasses often grew in “forests” that regularly surpassed 3 feet tall and sometimes reached more than twice that high, the Atlantic hosted more diminutive “meadows” that rarely came close to that height. The genetic differences also aligned with the total biomass of eelgrass. In the Atlantic, evolutionary genetics and the present-day environment played equally strong roles in eelgrass biomass. In the Pacific, genetics had the upper hand. These impacts flowed up to other parts of the ecosystem as well. When it came to small animals that lived in the eelgrass, like invertebrates, the genetic signature from the Pleistocene again played a stronger role than the environment in the Pacific—while the two played equally strong roles in the Atlantic. “The ancient legacy of this Pleistocene migration and bottleneck of eelgrass into the Atlantic has had consequences for the structure of the ecosystem 10,000 years later,” Duffy said. “Probably more than 10,000.” Conserving the future That ancient genetics can play such a strong role—sometimes stronger than the environment—has some ecologists concerned about whether eelgrass can adapt to more rapid changes. “Climate warming—by itself—is probably not the primary threat for eelgrass,” Olsen said. Pollution from cities and farms, which can cloud the water and lead to harmful algal blooms, also endangers seagrasses. That said, the vast array of environments eelgrass can survive in testifies to its hardiness. “I’m hopeful because our results illustrate long-term resiliency to repeated, major changes in thermal tolerances and the wide range of eelgrass habitats over about half the Northern Hemisphere,” Olsen said.

